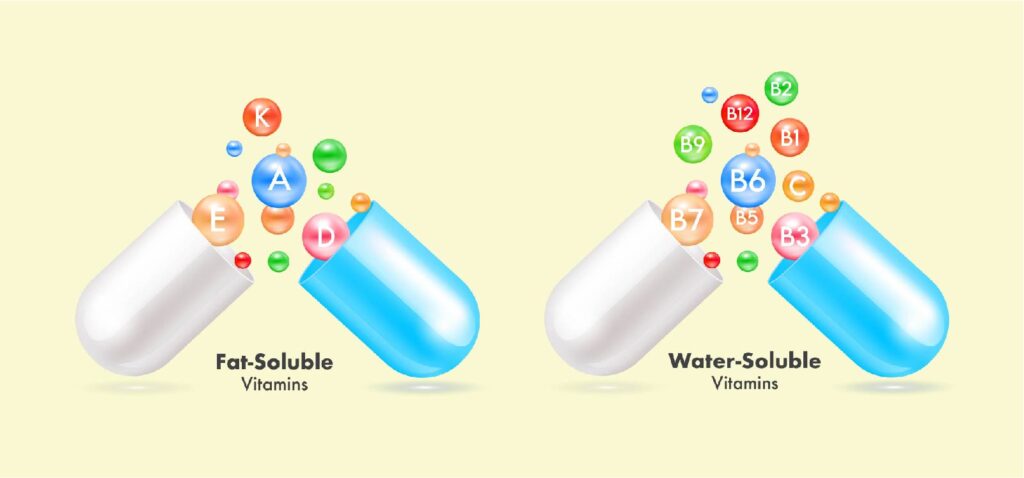
We’ve been told to “eat a rainbow” and incorporate a variety of colorful foods into our diet for good reason. Vividly colored plants contain phytonutrients, including carotenoids, which offer a spectrum of health benefits—from supporting vision and skin, to promoting heart and brain health, to combating oxidative stress and protecting cells, to lowering risk for a variety of health conditions.