Have you ever wondered how your body maintains a delicate balance, ensuring that various processes function smoothly? It turns out that there’s a fascinating system within our bodies called the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) that plays a crucial role in maintaining overall harmony. In this blog, we’ll explore the Endocannabinoid System in simple terms, so you can better understand this intricate internal mechanism.
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
The Endocannabinoid System is a complex network of receptors, enzymes, and molecules spread throughout our body. It is responsible for regulating various functions such as mood, sleep, appetite, pain sensation, immune response, and more. The ECS acts like a communication system, ensuring that different systems in our body work together in harmony.
The Components of the Endocannabinoid System
- Receptors: The ECS has two primary types of receptors, known as CB1 and CB2 receptors. CB1 receptors are mainly found in the brain and central nervous system, while CB2 receptors are primarily present in the immune system and peripheral tissues. When these receptors are activated, directly or indirectly, they trigger specific responses in the body.
- Endocannabinoids: Endocannabinoids (by definition, “endo” means “within”) are naturally occurring compounds produced within the body. The two most well-known endocannabinoids are anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). These endocannabinoids bind to CB1 and CB2 receptors, helping to regulate various bodily functions.
- Enzymes: Enzymes are responsible for breaking down endocannabinoids once they have completed their tasks. Two key enzymes involved in this process are fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), which breaks down anandamide, and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL), which breaks down 2-AG.
How Does the Endocannabinoid System Work?
The ECS functions through a process known as retrograde signaling. When a certain part of our body experiences imbalance or stress, endocannabinoids are produced and activate CB1 or CB2 receptors. This binding or activation triggers a response, which aims to restore equilibrium and bring the body back to a balanced state. For instance, if you experience pain, endocannabinoids may be released to reduce the pain sensation. Additionally, the ECS broadly interacts with numerous receptors of other signaling systems, which can provide overlapping functions, such as in pain, inflammation, sedation, anxiety, and neuroprotection.
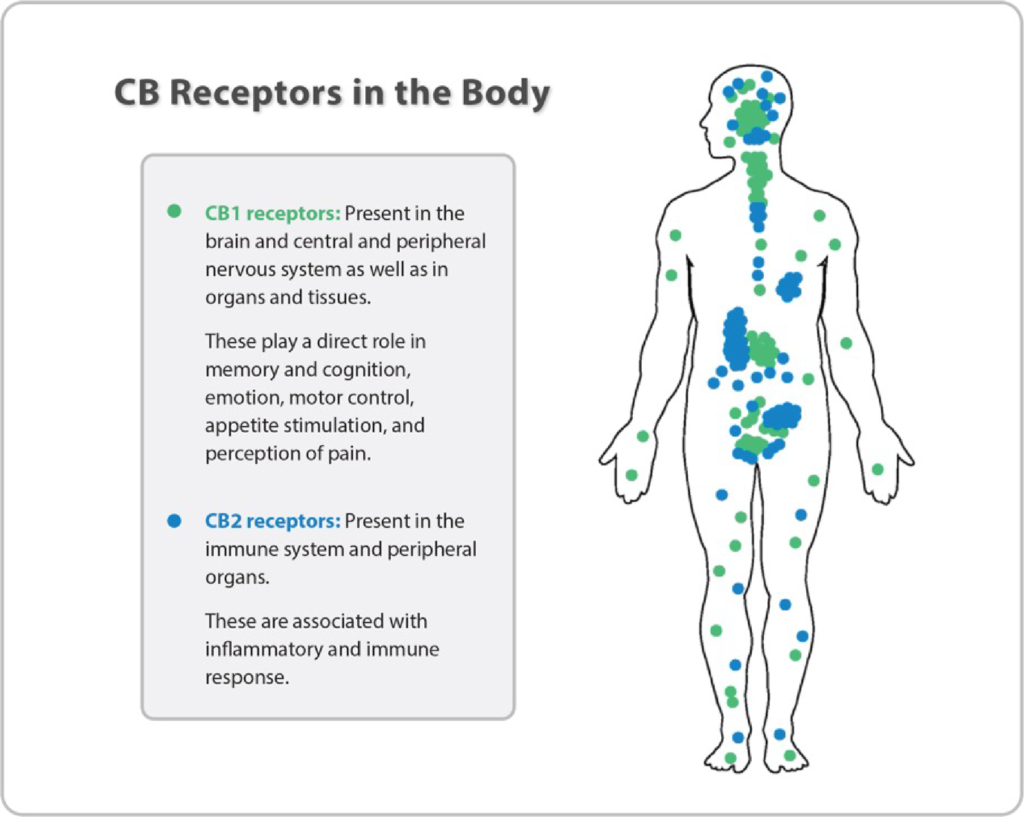
Why is the Endocannabinoid System Important?
The Endocannabinoid System is involved in a wide range of physiological processes, contributing to our overall well-being. It helps regulate mood, promoting feelings of happiness and relaxation. It also plays a role in appetite regulation, influencing hunger and satiety cues. Moreover, the ECS is involved in the modulation of the immune system, assisting with inflammation and immune response.
Supporting a Healthy Endocannabinoid System
Certain lifestyle choices can influence the health, function and overall balance of the Endocannabinoid System. The state of the body’s ECS, also known as “ECS Tone,” is influenced by a variety of factors such as genetics, lifestyle, stress levels, diet, and overall health. When the ECS is in a state of balance or optimal tone, it functions effectively to promote overall well-being and support various bodily processes. On the other hand, if there is dysregulation in the ECS tone, meaning it is not producing sufficient endocannabinoids or the receptors are not functioning optimally, these imbalances may contribute to health issues. It’s important to note that ECS tone is a dynamic state that can fluctuate in response to internal and external factors. In addition to the endocannabinoids naturally produced within our bodies, it’s fascinating to note that certain plant compounds, known as phyto-cannabinoids (“phtyo” meaning “from a plant”), can also interact with the Endocannabinoid System and optimize ECS Tone. One well-known source of phyto-cannabinoids is hemp. Hemp-derived products, such as CBD, have gained popularity due to their potential therapeutic effects. When consumed, phyto-cannabinoids like CBD (cannabidiol) interact with CB1 and CB2 receptors, influencing the ECS’s activity and helping to restore balance. Learn more about replenishing the endocannabinoid system in this Bridging the Gap blog.
Beyond cannabinoids found in hemp, there are also other botanical phyto-cannabinoids that can interact with the ECS. Some examples include compounds found in plants such as echinacea, black pepper, and clove. These plants contain compounds that can mimic the actions of endocannabinoids and interact with ECS receptors. Further, certain ingredients like beta-caryophyllene, a terpene found in various plants including black pepper and hops, can also activate ECS receptors. Exploring these alternative botanical options provides an exciting avenue for potential ECS modulation and therapeutic benefits.
Growing focus on this fascinating system
The Endocannabinoid System was discovered in the 1990s, and it has received increased attention and understanding in recent years due to the growing interest in cannabis research and the potential therapeutic applications of cannabinoids. It is a remarkable internal system that helps maintain balance and harmony within our bodies. By understanding its role and supporting its health, we can promote overall well-being. Although further research is needed to unlock the full potential of the ECS, it is clear that this intricate system contributes to our daily functioning and deserves our attention.