Behind every heartbeat, muscle movement, and burst of energy is Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) — a behind-the-scenes nutrient found in nearly every cell of the body. CoQ10 plays a vital role in overall health, especially mitochondrial energy and antioxidant defense. Let’s break down the science behind CoQ10 and its active form, ubiquinol, explore how they work in the body, and understand how they optimize cellular energy and defend the body against oxidative stress.
Ubiquinone and Ubiquinol
CoQ10 has two primary forms – ubiquinone and ubiquinol. Ubiquinone is the oxidized form, and ubiquinol is the reduced, biologically active form used by body. While ubiquinone must first be converted into ubiquinol, ubiquinol is immediately active, allowing it to be more readily utilized at the cellular level. Within the body, CoQ10 continuously cycles between these two forms as needed.
The names ubiquinol and ubiquinone come from the word ubiquitous, meaning “present everywhere.” This naming reflects the fact that CoQ10 is found in virtually every cell of the human body. It is especially concentrated in tissues with high energy demands, such as the heart, brain, liver, and skeletal muscle. As such, CoQ10 supports multiple functions, including exercise performance and recovery, cognitive performance and cardiovascular health. Yet, its two primary functions are mitochondrial energy production and antioxidant activity.
Antioxidant activity
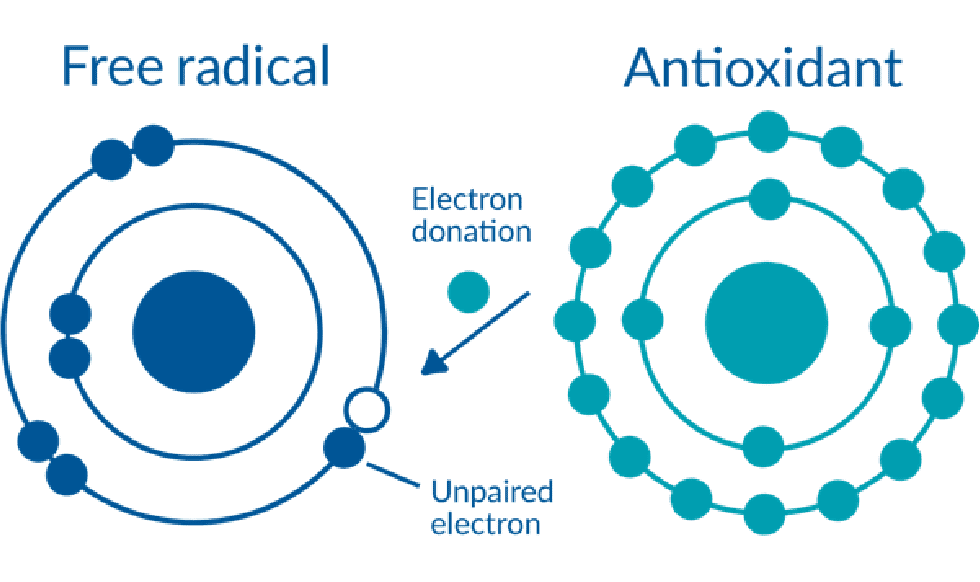
Ubiquinol acts as a powerful antioxidant by donating not one, but two electrons to stabilize free radicals. By actively neutralizing these unstable molecules, ubiquinol helps protect cells, proteins and DNA from oxidative damage. Ubiquinol is particularly useful in mitochondria, which are one of the primary sources of harmful free radicals, especially reactive oxygen species (ROS). Ubiquinol is conveniently concentrated near the source of ROS, in lipid-rich mitochondrial membranes, making it the ideal candidate for neutralizing free radicals and preventing damage to the very structures that produce cellular energy.
Mitochondrial energy production
Ubiquinol is a critical part of the electron transport chain, the series of reactions in mitochondria that produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell’s primary energy currency. By shuttling electrons between complexes I/II and III, ubiquinol enables efficient ATP synthesis, ensuring that high-energy tissues like the heart, brain, and muscles have the fuel they need.
Ubiquinol also supports mitochondrial homeostasis – the process of maintaining healthy and balanced cells and mitochondria. It does this by promoting the quality and quantity of mitochondrial functions including fission and fusion, apoptosis and mitophagy, and senescence. By optimizing mitochondrial health and efficiency, ubiquinol helps boost energy and combat fatigue.
Who is it for?
In healthy young individuals, the body efficiently converts ubiquinone into ubiquinol. However, conversion becomes less efficient with age and under conditions of increased oxidative stress. Endogenous CoQ10 production also declines naturally with age, and levels can be reduced by chronic stress, certain health conditions, and statin therapy.
As such, a ubiquinone supplement (traditionally labeled as CoQ10) may be appropriate for younger adults, individuals with no known absorption issues or those seeking foundational mitochondrial support. Ubiquinol may be preferred for adults over 40, individuals taking statins, those seeking enhanced antioxidant protection, or people with higher energy requirements or oxidative stress.
Takeaway
CoQ10 and its active form, ubiquinol, are fundamental to cellular health, supporting efficient mitochondrial energy production while helping protect cells from oxidative damage. Although natural CoQ10 levels decline with age, supplementation may be a practical solution to maintaining healthy levels and for sustaining energy and long-term cellular resilience.
Before beginning any new supplement, including CoQ10 or ubiquinol, speak with a healthcare provider to ensure it’s appropriate for your individual health needs.
References
Beckman KB, Ames BN. The free radical theory of aging matures. Physiol Rev. 1998;78(2):547-81.
Bentinger M, Brismar K, Dallner G. The antioxidant role of coenzyme Q. Mitochondrion. 2007 Jun;7 Suppl:S41-50.
Bratic A, Larsson NG. The role of mitochondria in aging. J Clin Invest. 2013 Mar;123(3):951-7.
Ernster L, Forsmark-Andrée P. Ubiquinol: an endogenous antioxidant in aerobic organisms. Clin Investig. 1993;71(8 Suppl):S60-5.
Kalen A, Appelkvist E-L, Daliner G. Age-related changes in the lipid compositions of rat and human tissues. Lipids. 1989;24(7):579-584.
Pallotti F, Bergamini C, Lamperti C, Fato R. The Roles of Coenzyme Q: Involvement in Cellular Functions. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 23;23(1):128.

